How to Accurately Find Percent Yield: A Simple Guide for 2025
Understanding how to calculate percent yield is essential for anyone studying chemistry. This value allows chemists and students to assess the efficiency of their experiments. This guide will simplify the concept of percent yield calculation, providing clear examples and insight into the factors that influence yield outcomes.
What is Percent Yield?
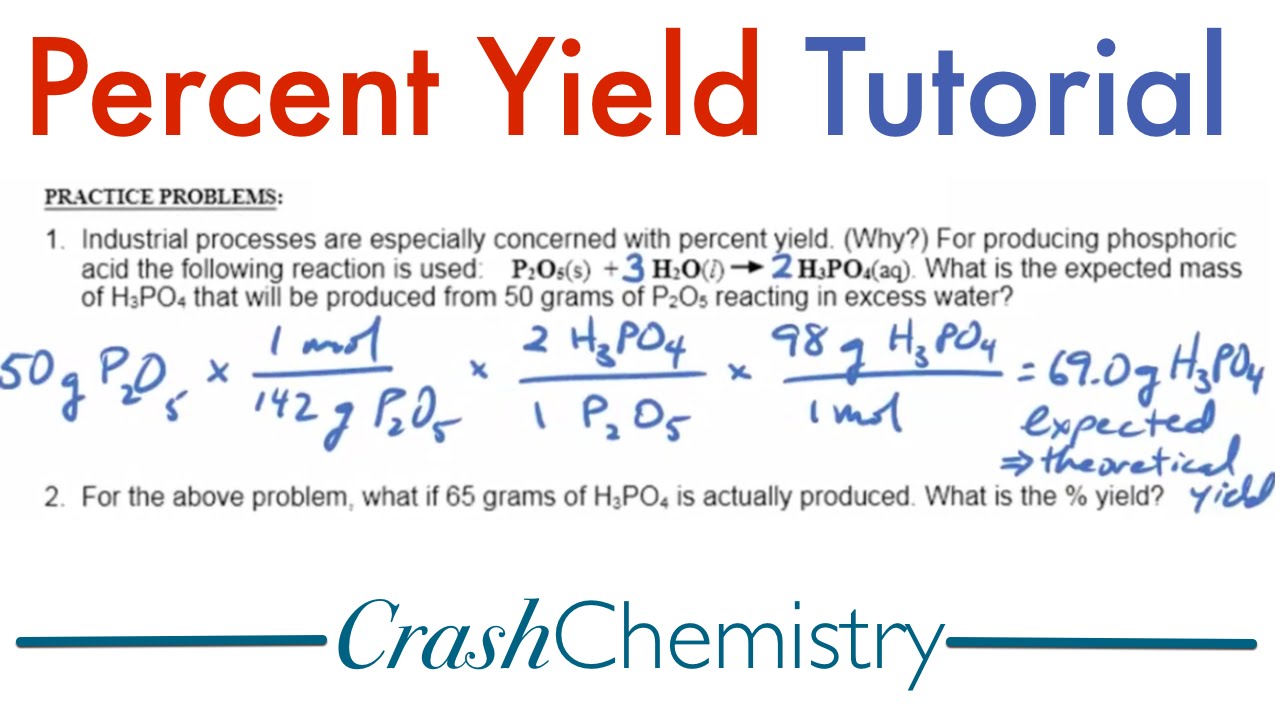
The percent yield definition refers to the amount of product obtained from a chemical reaction relative to the theoretical maximum amount of product expected. This is crucial in chemistry because it provides a clear measure of how effectively a reaction is executed. The percent yield formula is calculated using the equation:
Percent Yield = (Actual Yield / Theoretical Yield) x 100
In this formula, the actual yield is the measured production from the reaction, while the theoretical yield is the predicted amount based on stoichiometric calculations. For example, if a reaction theoretically should produce 10 grams of a product, but the actual yield is only 8 grams, the percent yield would be 80%. This simple percentage gives researchers insight into the reaction’s efficiency.
Why is Percent Yield Important?
Understanding importance of percent yield lies in its application to both academic and industrial chemistry. It helps scientists evaluate the effectiveness of their procedures, making it a fundamental component in planning and executing chemical reactions. Monitoring percent yield not only aids in enhancing lab efficiency but also empowers researchers to optimize their experiments and resource utilization. Furthermore, in chemical manufacturing processes, maintaining high percent yields can significantly reduce costs and waste, driving better environmental consciousness within industries.
Common Percent Yield Problems
Many chemistry students often face percent yield problems that challenge their understanding. A typical task might involve a given theoretical yield and actual yield, asking students to find the corresponding percent yield. These exercises are essential in fostering a strong grasp of both concepts and applications, reinforcing the link between theoretical calculations and real-world lab scenarios.
How to Calculate Percent Yield?
To methodically approach finding percent yield, one can follow a straightforward method. Begin by gathering the following information: the actual yield obtained from your experiment and the theoretical yield determined through stoichiometric calculations. Once you have these values, you can plug them into the percent yield equation mentioned previously.
Step-by-Step Example Calculation
Let’s walk through a simple example. Imagine you conducted a chemical reaction designed to produce a specific compound. After measuring the final product, you find an actual yield of 45 grams. Calculating the theoretical yield yields 60 grams. Now, using the percent yield calculation help:
- Use the equation: Percent Yield = (45 grams / 60 grams) x 100.
- Calculating this gives: Percent Yield = (0.75) x 100 = 75%.
This demonstrates that the reaction produced 75% of what was theoretically possible, providing crucial feedback for future experimental design.
Factors Affecting Percent Yield
Several factors affecting percent yield can influence the efficiency of chemical reactions. Some key factors include the purity of reactants, reaction conditions (temperature, pressure, and pH), and the completion of the reaction. If reactants are impure, this may lead to unpredicted side reactions, lowering the overall yield. Additionally, a reaction not proceeding to completion (often referred to as equilibrium shifting) can dramatically affect the actual to theoretical yield ratio.
Improving Percent Yield
To achieve a higher calculated percent yield, chemists often focus on optimizing several experimental conditions. Strategies may involve pure reactants, adjusting temperature presets, altering concentration levels, or fine-tuning reaction times.
Best Practices for Maximizing Yield
Here are several practical applications of yield percentage strategies:
- Always use the highest purity reagents available.
- Maintain controlled and consistent temperatures during the reaction.
- Monitor reaction times closely to prevent side reactions.
- Post-reaction, ensure efficient isolation methods to minimize product loss.
Experimental Yield Tracking
Experimental yield tracking is crucial to identify trends and improve future experiments. By systematically recording both actual and theoretical yields, researchers can analyze performance over time, helping pinpoint areas for improvement. Charts and graphs can effectively visualize yield data leading to easy comparisons, shedding light on which methods yield the best outcomes.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding how to accurately find percent yield not only enriches knowledge in chemistry but also solidifies critical laboratory skills. By grasping the percent yield definition, calculating with accurate formulas, and implementing best practices, students and researchers can greatly improve their experimental outcomes.
FAQ
1. What is the relationship between actual yield and theoretical yield?
The actual yield is the quantity of product produced from a chemical reaction, verified through measurement, while the theoretical yield represents the calculated maximum that could be produced based on the reaction’s stoichiometry. The relationship is vital for determining the percent yield which reflects the efficiency of the reaction.
2. How can I identify discrepancies in yield?
To identify discrepancies in yield, consider comparing actual yields from similar reactions, analyzing reaction conditions, and evaluating reactant purity. Using these assessments will highlight areas needing adjustment and can help diagnose why yields may deviate from expected norms.
3. Why might percent yield be low in my experiment?
A low percent yield can arise from several issues like incomplete reactions, impure reactants, side reactions, or losses during recovery and purification processes. Identifying and mitigating these factors is crucial for meeting yield expectations in laboratory settings.
4. What resources are helpful for yield calculations?
Numerous resources, including academic journals, online calculators, and detailed textbooks, provide enriching content about yield calculations in chemistry. Websites dedicated to educational content often offer calculators and tutorial articles that can aid in understanding complex yield scenarios.
5. Can yield percentages vary across different reactions?
Yes, yield percentages can significantly vary due to numerous factors including the type of reaction, reactants used, and overall experimental conditions. Surveys examining past yields can provide averages for specific reactions in particular environments, allowing chemists to establish expected performance metrics.
6. What role does temperature play in percent yield calculations?
Temperature significantly impacts reaction rates and equilibrium. If a reaction is exothermic, lowering the temperature may shift the equilibrium towards the reactants, reducing actual yield. Similarly, reactions sensitive to temperature conditions can influence the efficiency assessed through percent yield.
7. How can I effectively interpret yield results?
To interpret yield results effectively, it’s important to analyze them in the context of expected performance based on theory and prior empirical data. Comparing current yield outcomes to historical data can inform adjustments or confirm successful methodologies.
For anyone interested in deepening their understanding of percent yield, exploring supportive material or practice problems is highly encouraged.