Effective Ways to Find the Horizontal Asymptote
Understanding Horizontal Asymptotes
To grasp the concept of a **horizontal asymptote**, one must first understand its definition and significance in calculus and graphing. A horizontal asymptote represents a horizontal line that the graph of a function approaches but may not necessarily touch as the input values approach infinity. It is crucial in determining the **end behavior** of functions, particularly **rational functions**. Knowledge of horizontal asymptotes is vital for analyzing **function behavior**, as it offers insights into how functions behave as they extend infinitely in either direction. In this section, we will cover key rules and examples to contextualize this mathematical concept.
Horizontal Asymptote Rules
Several **rules** dictate how to determine the **horizontal asymptote** for rational functions. A fundamental guideline is based on the degrees of the polynomials in the numerator and denominator. If the degree of the numerator is less than that of the denominator, the horizontal asymptote is at \(y = 0\). Conversely, if the degree of the numerator equals that of the denominator, the horizontal asymptote is determined by dividing the leading coefficients of the polynomials. For cases where the degree of the numerator exceeds that of the denominator, no horizontal asymptote exists, although a **vertical asymptote correlation** may be present. Understanding these rules can pave the way for evaluating **horizontal asymptotes** effectively.
Applications of Horizontal Asymptotes
The concept of **horizontal asymptotes** extends beyond theoretical mathematics into real-life applications. They are integral in fields such as engineering, physics, and economics where rapid changes in data trends are evaluated. For instance, understanding the **horizontal asymptotic behavior** can assist in predicting the behavior of a system as it stabilizes over time. Applications can be observed in modeling natural phenomena, optimizing processes, or even in inventory management where limits play crucial roles. Additionally, humans have utilized the concept of **horizontal asymptotes in limits** to analyze systems that approach certain values without ever reaching them, thereby laying foundational concepts in **calculus** and related disciplines.
Techniques for Finding Horizontal Asymptotes
Knowing the rules for identifying **horizontal asymptotes** is just the beginning. There are several effective techniques that individuals can implement to find these crucial points in function behavior quickly. Using **algebraic techniques** and tools such as polynomial long division will not only enhance comprehension but also streamline the process of determining the horizontal outcome as input values become significantly large.
Using Polynomial Long Division
One of the most practical methods for determining a horizontal asymptote involves **polynomial long division**. This technique applies especially when the degree of the numerator exceeds that of the denominator. By dividing the numerator by the denominator, it becomes apparent which term dominates the function as it approaches infinity. The quotient will often yield a constant, which could indicate the line of the horizontal asymptote. Implementing **long division in calculus** allows for greater clarity when analyzing complex function limits, improving your understanding of **graph behavior** within the context of curves.
Limit Evaluation at Infinity
Another straightforward technique for identifying the **horizontal asymptote** of a function is to evaluate the limit of the function as \(x\) approaches infinity or negative infinity. Mathematically, this is represented as \( \lim_{x \to \infty} f(x) \). If this limit converges to a particular value, that value represents the **horizontal asymptote**. For example, in a function like \(f(x) = \frac{2x + 3}{4x + 5}\), evaluating the limits provides critical insights into **asymptotic behavior** that is essential in calculus concepts.
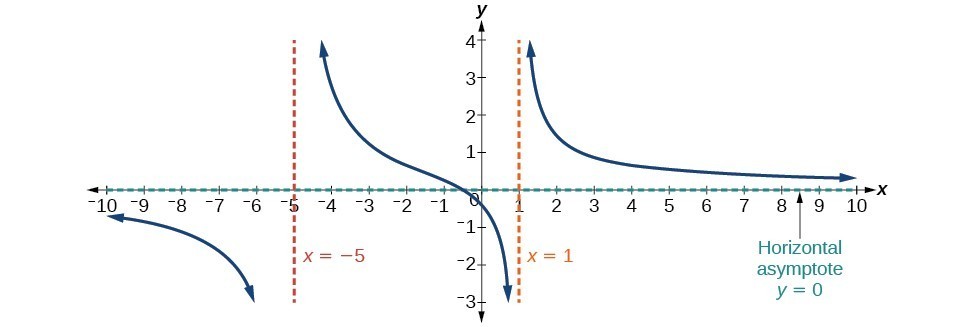
Graphing Horizontal Asymptotes
An effective way to visualize horizontal asymptotes and understand their roles in function analysis is through graphing. **Graphing rational functions** can significantly enhance comprehension of how these functions behave near their asymptotes. When one plots the function, the **asymptotes can serve as boundaries**, guiding the graph’s path towards infinity. Visualizing these asymptotes provides a rich context that is difficult to grasp solely through mathematical analysis.
Graphing Techniques for Asymptotes
To graph a rational function and effectively illustrate its **horizontal asymptotes**, one should first identify and plot the asymptotic lines based on previously discussed rules and limits. It can be helpful to utilize graphing calculators or computer software that allows for manipulative input conditions to quickly visualize **and understand limits**. This process not only aids in illustrating critical points but also strengthens one’s intuition for recognizing patterns and behaviors in function limits while transitioning towards infinity.
Analyzing Graph Behavior with Asymptotes
Once the horizontal asymptotes are plotted, analyzing the graph’s behavior around these lines illuminates profound insights into the nature of the function. Observing how the graph approaches or deviates from the **horizontal line** specified by the asymptote can significantly inform one’s understanding of limiting behavior. For instance, the examination of relevant functions within a specific context, such as the **function behavior of growth and decline**, provides a foundation for applying calculus techniques in real-time scenarios.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding and identifying horizontal asymptotes is crucial for analyzing the behavior of rational functions.
- Rules and techniques such as polynomial long division aid in determining horizontal asymptotes effectively.
- Graphing functions can enhance visualization and understanding of asymptotic behavior and limits.
- Real-world applications highlight the significance of horizontal asymptotes in various fields, from engineering to economics.
- Evaluating limits at infinity provides a clear method for finding horizontal asymptotes directly.
FAQ
1. What is the horizontal asymptote definition?
The **horizontal asymptote** is a horizontal line that a function approaches as the variable moves towards positive or negative infinity. Understanding this concept is vital in analyzing **function limits** and overall behavior of rational functions.
2. How can I calculate my function’s horizontal asymptote?
To **calculate horizontal asymptotes**, examine the degrees of the numerator and denominator in a rational function. Use the rules explained to determine their respective limits as \(x\) approaches infinity to identify the asymptote’s value.
3. What role does limit evaluation play in identifying asymptotes?
**Limit evaluation** serves as a primary method for determining a function’s horizontal asymptote. By calculating the limit of the function as \(x\) approaches infinity, you can ascertain the specific value that defines the horizontal boundary of that function.
4. Why is the horizontal asymptote significant in calculus?
The **significance of horizontal asymptotes** in calculus lies in their ability to help predict the behavior of functions at extreme values. They facilitate a better understanding of function stability and trends, serving as essential tools in applied mathematics.
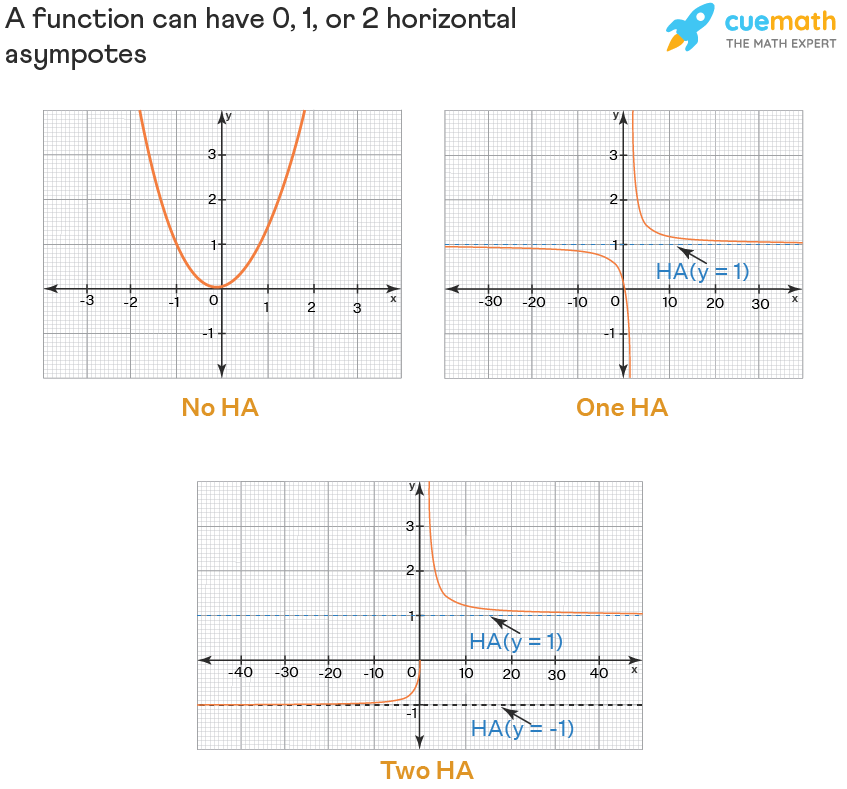
5. Can there be multiple horizontal asymptotes?
Typically, a function will have no more than one **horizontal asymptote** due to the properties of limits approaching infinity. However, cases with piecewise functions might show variations that call for analyzing each segment individually.
6. How do I graph a rational function with horizontal asymptotes?
To graph a rational function with intuited **horizontal asymptotes**, start by plotting the asymptote lines. Then graph the function by focusing on critical points, using a graphing calculator may further provide clarity.
7. How do horizontal asymptotes differ from vertical asymptotes?
**Horizontal asymptotes** describe behavior at the extremities of function values, conveying end behavior, while **vertical asymptotes** indicate where the function becomes undefined or approaches infinity due to division by zero. The analysis of both is crucial for a comprehensive understanding of a function’s behavior.