“`html
Effective Ways to Find Cumulative Frequency in 2025: Practical Steps to Master the Concept
Cumulative frequency is a fundamental concept in statistics, essential for understanding data distribution and represents the cumulative total of frequencies up to a certain point in a data set. This guide offers effective techniques and practical methods to help you master cumulative frequency in 2025, enhancing your data analysis skills and improving your ability to interpret statistical information.
Understanding Cumulative Frequency
To effectively tackle cumulative frequency, it’s crucial to first grasp its definition and significance within the context of statistics. **Cumulative frequency** refers to the running total of frequencies up to a particular data point. This method is invaluable when compiling a **frequency distribution** that summarizes data points and their respective counts. By familiarizing yourself with this concept, you can better analyze **numerical data** for trends and insights. The process encourages an organized approach to **data analysis**, enabling the visualization of cumulative data through various representations such as tables and graphs.
What is Cumulative Frequency?
**Cumulative frequency** allows statisticians and researchers to see how many data points fall below a certain value in a dataset. It is a way of summarizing data by providing a running total of the frequency counts. This is particularly useful in creating a **cumulative frequency table** where values are listed alongside their corresponding cumulative totals. Understanding this foundational concept is key when moving on to more complex techniques such as **calculating cumulative frequency** for various datasets, which can help you identify patterns and distributions effectively.
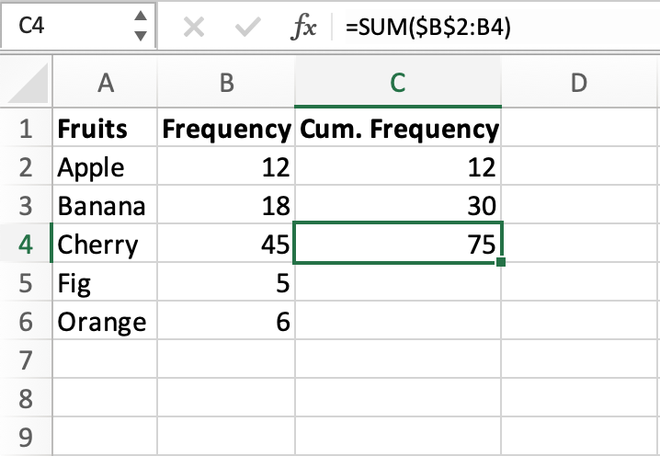
Creating a Cumulative Frequency Table
The first practical step in applying cumulative frequency is constructing a **cumulative frequency table**. This involves two main actions: organizing your data, and then calculating the totals. Start by listing your data in ascending order. Next, for each value, add the frequency counts of previous values to get the cumulative total. For example, suppose you have a dataset on the number of books read by a group: 1, 3, 2, 4, and 5 with the following frequencies: 1, 2, 3, 2, and 1, respectively. The cumulative frequencies will therefore be 1, 3, 5, 7, and 8. This provided clarity and allows for easy interpretation of **frequency distribution**.
Applications of Cumulative Frequency in Data Visualization
Visualizing cumulative frequency can significantly enhance your understanding of data trends. Creating a **cumulative frequency graph** or **cumulative frequency curve** can illustrate the distribution of the data, highlighting how many observations fall below a certain value. This graphical data representation can help you easily perceive patterns and key statistical insights. For example, plotting a **cumulative frequency graph** allows observers to quickly determine quartiles and make further calculations necessary for deriving the **mean calculation** and **median calculation** in practical scenarios.
Calculating Cumulative Frequency for Different Data Types
Cumulative frequency is versatile and can be applied across various datasets—whether they are grouped or ungrouped. Calculating cumulative frequency varies slightly depending on the nature of the data, requiring different approaches for handling discrete or continuous data sets.
Cumulative Frequency in Discrete Data Sets
When dealing with discrete data, the method of calculating cumulative frequency remains straightforward. As highlighted previously, you simply add the frequency of each value successively. For example, in a frequency chart for students who scored 70, 80, and 90 with corresponding **frequency counts** of 5, 10, and 15, your cumulative frequencies will be 5, 15, and 30. This simple addition allows quick analysis of **cumulative data** and helps identify trends and distributions associated with performance metrics.
Grouping Data for Cumulative Frequency Calculations
For large datasets, it may be beneficial to group the data into intervals when calculating cumulative frequency. This is particularly advantageous in fields like educational statistical analysis where student scores are grouped into ranges. For instance, if data on test scores are presented in groups (60-69, 70-79, etc.), you can calculate the **cumulative frequency** by summing the frequencies of each group as you progress downwards. As a result, understanding the overall performance of a population becomes seamless.
Importance of Cumulative Frequency in Statistical Analysis
Utilizing cumulative frequency can greatly enhance statistical analysis. Understanding **cumulative frequencies** aids in descriptive statistics and aids in presenting data effectively. The implications of cumulative frequency extend into various applications within **frequency analysis** including public health, education, and economic statistics, guiding organizations in interpreting large sets of data to inform decisions. This methodology can also be applied when constructing **histograms** or when relevant insights are needed from more complex statistical computations such as variance and standard deviation.
Graphs and Visual Representation of Cumulative Frequency
The use of graphs is integral to comprehending data distributions visually. Through cumulative frequency graphing techniques, users can create compelling visualizations that reflect trends in their data, aiding in both interpretation and presentation to stakeholders.
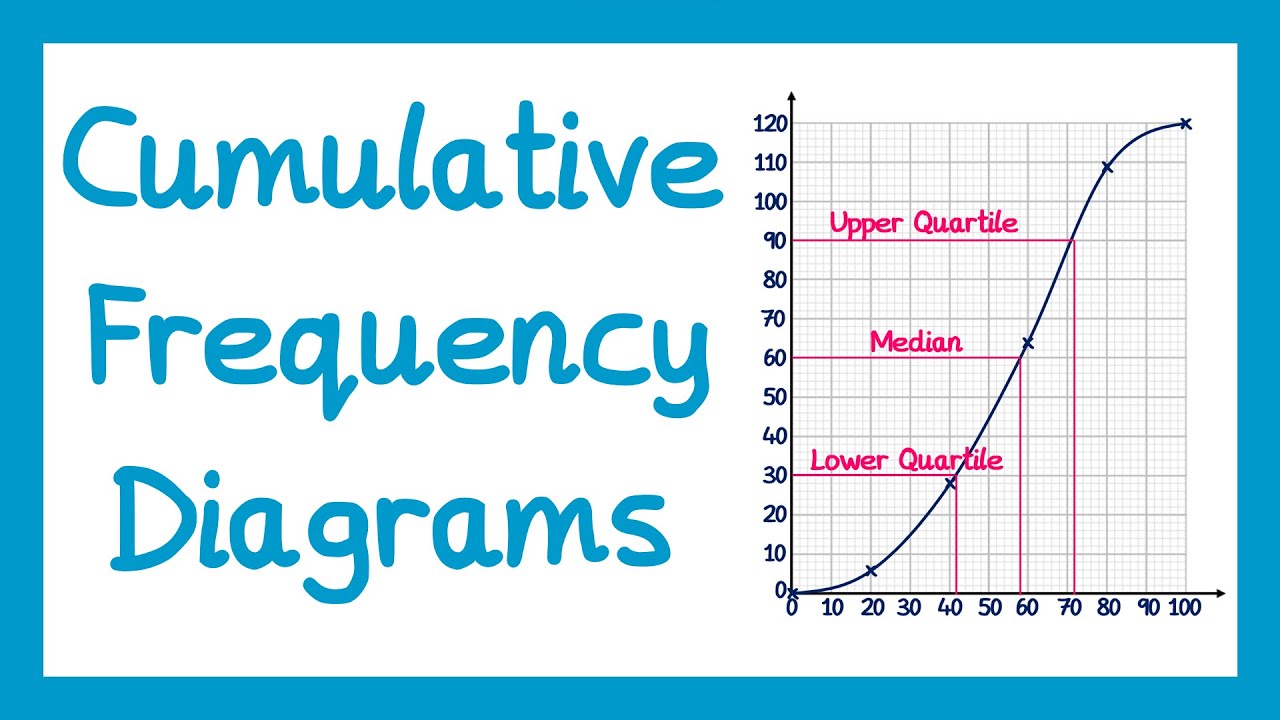
Constructing a Cumulative Frequency Graph
To produce an effective **cumulative frequency graph**, you should first construct your cumulative frequency table. Plot the cumulative frequencies against the upper boundaries of the data intervals (or values) on a graph. Since the graph illustrates the cumulative total, each point will reflect an accumulation. Connecting these points provides a clear visual representation, quickly showing trends in data. For example, in educational data analysis, visualizing results through a cumulative frequency graph can help educators comprehend performance levels more clearly than raw numerical presentations.
Understanding Cumulative Frequency Curves
A **cumulative frequency curve** is another effective tool that can complement graphs. By plotting cumulative frequencies, you create an S-shaped curve that clearly defines the probability distribution. This popular graphing method in statistics helps interpretations of data more intuitively, indicating how data is distributed and revealing significant data trends. Understanding these curves is also beneficial for advanced statistical techniques such as determining percentiles and quartiles.
Using Frequency Polygons to Present Cumulative Data
Frequency polygons can also be utilized to depict cumulative frequency robustly. By connecting the midpoints of the intervals in your data with straight lines—after plotting the frequency—you can visualize how frequencies cumulate. It gives a more dynamic portrayal of what is essentially a histogram and can easily illustrate changes in data trends. Utilizing polynomials can enhance the data presentation quality especially during analytical discussions, making it easier to convey points to any audience.
Key Takeaways
- Cumulative frequency is essential for organizing data and recognizing distribution patterns.
- Creating **cumulative frequency tables** is foundational for succeeding in **data analysis** techniques.
- Visualization methods such as graphs and polygons enhance data interpretation and term clarity.
- Different types of cumulative frequencies apply to both discrete and grouped data for versatility in analysis.
- Understanding these principles aids significantly in advanced statistical concepts and practical applications.
FAQ
1. How do I calculate cumulative frequency for grouped data?
To calculate cumulative frequency for grouped data, first create a table listing the class intervals along with their corresponding frequency counts. Then, to find cumulative frequency, add the frequency of the first group to the cumulative total of prior groups progressively. For instance, if the frequency of groups is 5, 10, and 15 for the intervals 60-69, 70-79, and 80-89, the cumulative frequencies will be 5, 15, and 30 respectively, providing a clear representation of how data accumulates.
2. What is the difference between cumulative frequency and relative frequency?
Cumulative frequency totals all frequencies for categories leading up to a specific point, showing how many data points fall below a given value. Conversely, relative frequency expresses how often an event occurs relative to the total number of entries, essentially showing proportions rather than totals. Both forms of frequency analysis are crucial for a complete understanding of datasets, but they serve different purposes in statistical evaluations.
3. Can cumulative frequency be used for qualitative data?
Cumulative frequency is primarily applied to quantitative data, as it requires numerical values to sum up frequencies. However, in some cases, you may convert qualitative data into quantitative forms through ranking or encoding, thus allowing for a cumulative frequency analysis of those transformed datasets. It’s crucial to interpret qualitative occurrences accurately to retain the integrity of the analysis.
4. What are the real-world applications of cumulative frequency analysis?
Cumulative frequency analysis finds applications in various fields such as education, public health, business sales analysis, and research, where summarizing and interpreting large quantities of quantitative data is essential. For instance, schools may use this analysis to track student performance across different grades, helping identify trends and areas requiring improvement for future curriculum adjustments.
5. How can I visualize cumulative frequency effectively?
To visualize cumulative frequency effectively, consider using cumulative frequency graphs, curves, or frequency polygons that depict the data well visually. These graphs allow you to see data trends at a glance, facilitating easier analysis. Utilize software tools such as Excel or specialized statistical programs to create these visualizations effectively, making it simpler to present findings to an audience or utilize them in reports.
“`
