“`html
How to Properly Find LCM: 5 Effective Methods for Quick Calculation in 2025
Understanding LCM: Definition and Properties
The **Least Common Multiple (LCM)** is an essential concept in mathematics that highlights the smallest positive integer divisible by a given set of integers. Understanding **LCM properties** is vital as it plays a crucial role not only in number theory but also in real-life applications such as scheduling and problem-solving. For example, when determining deadlines for multiple projects, finding the **LCM of two numbers** can help establish common milestones. This article explores five effective methods to achieve quick and accurate **LCM calculations**, ensuring robust comprehension of **finding LCM** in various contexts.
What is LCM? A Closer Look
The **LCM** of a set of numbers is characterized by its relationship with other mathematical concepts, like the **Greatest Common Divisor (GCD)**. Specifically, the product of the **LCM and GCD** of any two integers equals the product of the integers themselves. This fundamental relationship simplifies many LCM problems, offering a pathway for efficient calculations. By grasping **LCM definitions** and the underlying principles, students can tackle more complex problems, including finding the **LCM of three numbers** with confidence.
Properties of LCM: Why They Matter
Key **LCM properties** include that it is always greater than or equal to the highest of the numbers whose LCM is being calculated. Additionally, if one number perfectly divides another, then the LCM is the larger number. Recognizing these properties is instrumental in effectively applying **LCM rules** in practical situations and enhancing one’s problem-solving skills. When tackling mathematical exercises involving LCM, it is beneficial to remember these properties for efficient and accurate results.
Five Effective Methods to Find LCM Quickly
There are multiple approaches to calculating the LCM. This section focuses on five critical methods: through prime factorization, listing of multiples, using the GCD, standard **LCM formulas**, and employing LCM calculators. Each method suits different scenarios and personal preferences, which can enhance the **LCM calculation** experience. Let’s dive into each technique to understand its application better.
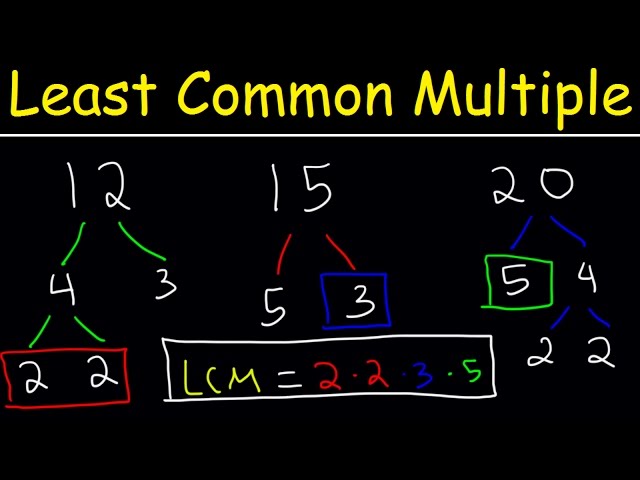
1. LCM Using Prime Factorization
**LCM using prime factorization** involves breaking down each number into its prime factors. For instance, to find the **LCM of two numbers** like 8 and 12, we start with their prime factorization: 8 = 2³ and 12 = 2² x 3¹. By taking the highest power of each prime factor, we calculate LCM as: LCM = 2³ x 3¹ = 24. This method is particularly effective for numbers with larger values as it organizes the calculation visually and simplifies the process.
2. LCM Through Listing Multiples
The **listing multiples** method is straightforward and effective, particularly for small numbers. To find the LCM of 4 and 5, simply list the multiples: Multiples of 4: 4, 8, 12, 16, …; Multiples of 5: 5, 10, 15, 20, … The first common multiple is 20, making the **LCM 20**. Though less efficient for larger numbers, listing multiples can provide immediate insights into patterns, enhancing understanding during initial learning phases.
3. Utilizing GCD for LCM Calculations
The formula **LCM = (a * b) / GCD(a, b)** offers a relationship-driven approach. For instance, to calculate the **LCM of two numbers**, say 20 and 30, first determine their GCD, which is 10. Therefore, LCM = (20 * 30) / 10 = 60. This method is especially useful when dealing with larger numbers as it significantly cuts down time and experimentation involved in multiple listings.
4. Implementing a Standard LCM Formula
In many mathematical scenarios, knowing a standard **LCM formula** can expedite calculations. For three numbers, for instance, the formula is expressed as LCM(a, b, c) = LCM(LCM(a, b), c). If we seek the **LCM of 3, 4, and 5**, we can first find the LCM of 3 and 4, yielding 12, and then apply the formula again with 5: LCM(12, 5) = 60. This layered approach is beneficial in more complex problems where multiple numbers are involved.
5. Utilizing LCM Calculators
Today, technological advancements offer ease through **LCM calculators** available online. These tools allow anyone to input numbers and swiftly compute their LCM, making it a go-to approach for students and professionals pressed for time. While understanding the fundamental concepts behind LCM is essential, using technology can efficiently enhance productivity without compromising learning goals.
Practical Applications of LCM
Understanding the significance of **LCM** is pivotal, as its applications extend beyond the classroom. In real-life, contexts like scheduling events, resolving conflicts, and working within systems can all require an efficient understanding of least common multiples. Distinguishing how to apply LCM in various situations equips individuals with practical tools to navigate complex everyday mathematics.
LCM in Real-Life Situations
The most common application of the **LCM** manifestly surfaces in scheduling. If two events are set to occur in regular intervals, such as every 4 days and every 6 days, finding the **LCM** helps identify when both events will coincide, essential for planning. In the example, the **LCM of 4 and 6** is 12, meaning both occurrences will align every 12 days.
Incorporating LCM in Number Theory
In advanced mathematics, particularly within number theory, the **LCM** holds strategic importance. Calculating the **LCM of algebraic expressions** or decimals aids in forming common denominators, essential in simplifying fractions and working with polynomials. Engaging with LCM within more complex realms solidifies one’s mathematical foundation, demonstrating how interconnected different mathematical principles are.
Key Takeaways
- A firm grasp of the **LCM definition** supports effective problem-solving across numerical scenarios.
- Multiple methods for **finding LCM** include prime factorization, listing multiples, GCD, standard formulas, and calculators.
- Real-life applications of LCM enrich comprehension and enhance practical mathematical skills.
FAQ
1. How do I find the LCM of fractions?
When finding the **LCM with fractions**, determine the LCM of the numerators and the GCD of the denominators. The formula then becomes: LCM = LCM(numerators) / GCD(denominators). Understanding this allows for effective management of mathematical expressions involving fractions.
2. Can I calculate LCM with decimals?
Yes, finding the **LCM of decimals** requires converting them into whole numbers by eliminating the decimal places (considering the least number of decimal places), followed by standard LCM methods. Once calculated, adjust the result back to accommodate the original decimal context.
3. What are LCM word problems?
**LCM word problems** illustrate real-world contexts in which finding an LCM is essential, typically involving scheduling or event alignment. These problems encourage practical application of mathematical principles, thus enhancing comprehension and immediate utility of knowledge.
4. Why are LCM visualizations helpful?
**LCM visualizations** help learners understand LCM concepts intuitively. Using diagrams or charts can clarify how LCM relates across different sets of numbers, enhancing memory through visual aids. This form of engagement is particularly useful in educational settings.
5. What is the main significance of understanding LCM?
Grasping **LCM significance in problem-solving** allows students and professionals to efficiently tackle mathematical challenges, facilitate coherent planning, and ensure accurate calculations required in various disciplines, ultimately fostering a deeper appreciation for mathematical intricacies.

“`
