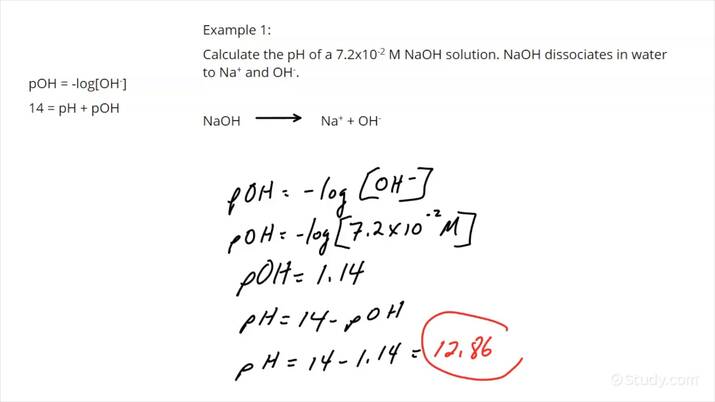How to Properly Calculate pH: A Practical Guide for 2025
Understanding how to calculate pH is essential in numerous fields, from chemistry to environmental science. Accurate pH measurement can influence various processes, such as brewing, agriculture, and environmental monitoring. This guide will explore different pH calculation methods, tools for measuring pH accurately, and the importance of pH in many applications, providing you with a comprehensive grasp of the subject.
pH Scale Explanation
The pH scale is a logarithmic scale used to specify the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. Ranging from 0 to 14, a pH of 7 is considered neutral. Values below 7 indicate acidity, while values above 7 indicate alkalinity. Understanding **the pH scale** is critical because it affects chemical properties and reactions, biological processes, and environmental conditions. For example, enzymes in biological systems often have optimal pH ranges, meaning precision in pH measurement is vital for laboratory and biological experiments.
Importance of pH in Chemistry
In chemistry, the importance of pH cannot be understated. pH levels influence reaction rates, solubility, and the stability of compounds. For instance, many chemical reactions are pH-dependent; acetic acid, for example, behaves differently at various pH levels. Understanding how pH affects chemical reactions is crucial in formulations across industries, such as pharmaceuticals, where precision impacts drug efficacy.
The pH Scale and Biological Systems
In biology, maintaining proper pH levels is essential for cellular functions and metabolic processes. The human body, for instance, relies on a tightly regulated pH around 7.4 to maintain homeostasis. Any deviations can result in health issues, making pH measurement a significant aspect of medical diagnostics and treatment. Accurate measurements can guide healthcare professionals in monitoring patients and making informed decisions on interventions.
pH Calculation Methods
Accurate pH measurement is achieved using various methods, including potentiometric measurements, indicator color comparisons, and calculation from concentration. Each method has its own advantages depending on the context. For example, pH meters are commonly used for their precision, while pH indicators provide visual cues for quick assessments in the field.
Measuring pH Accurately with pH Meters
pH meters are electronic devices designed to provide precise pH measurements. The best practices for their use include **calibrating pH meters** regularly to ensure accurate results. Calibration typically involves using standard buffer solutions to set the meter’s readings against known pH values. Upon calibration, the pH meter returns measurements based on the electrical potential generated by the pH-sensitive electrode immersed in the solution.
Indicators for pH Testing
Colorimetric methods using indicators for pH testing are another popular technique. These do not require as advanced equipment and can be visualized through the color change associated with specific pH levels. Common indicators include litmus paper and phenolphthalein. Each indicator has a limited range and works best in controlled conditions, making it essential to choose the right one depending on your needs.
Adjusting pH Levels and Applications
Adjusting pH levels is integral across numerous applications, including agriculture, brewing, and water treatment. Depending on the required acidity or alkalinity, adjustments can be made using various strategies, such as adding acids or bases to substances or employing buffer solutions to stabilize pH against fluctuations over time.
pH in Agriculture
In agriculture, soil pH plays a pivotal role in nutrient availability. For example, many nutrients become less available to plants when soil pH shifts too far from the neutral range. Regular soil pH measurement helps farmers and gardeners optimize growing conditions, improving crop yield and health. Soil amendments are often used to correct imbalances, such as applying lime to raise pH or sulfur to lower it.
pH in Brewing
For those interested in brewing, maintaining specific pH levels in solutions directly impacts flavor and fermentation processes. For example, during the mash stage of brewing beer, a pH between 5.2 and 5.6 promotes optimal enzymatic activity. Monitoring and adjusting during this and other stages ensures quality through precise flavor profiles, helping brewers elevate their craft.
Common Tools and Techniques for pH Testing
Various tools and equipment have emerged for effective pH measurement, ranging from basic pH testing kits to advanced laboratory-grade instruments. Understanding the types of tools available and how to use them can enhance the accuracy of pH readings and overall process management.
pH Testing Kits and Their Use
pH testing kits are available for home and lab use. These kits typically include pH measurement units, color-coded indicators, and testing solutions. Users can easily compare their sample against a color chart to gauge acidity levels. This method is particularly beneficial for home growers and educators demonstrating acidity across different liquids.
Daily pH Testing for Optimal Results
For applications such as aquaculture or pool maintenance, **daily pH testing** is practical for ensuring optimal conditions. In aquariums, maintaining stable pH levels can significantly influence fish health. Regular monitoring helps in making timely adjustments to keep environments healthy and sustainable.
FAQ
1. What is the significance of pH in environmental science?
In environmental science, pH levels influence the health of aquatic ecosystems. Acidic conditions can harm aquatic life by altering habitat availability and affecting species reproductive rates. Monitoring pH helps assess water quality and can guide remediation strategies for polluted ecosystems.
2. How can I choose the right pH indicator for my experiment?
When choosing a pH indicator, consider the pH range of your solution. Different indicators have specific color change thresholds that are effective at different pH levels. It’s essential to ensure that the indicator you select is suitable for the expected pH range in your testing process.
3. What role does temperature play in pH measurement?
Temperature can significantly impact pH measurements as it affects the dissociation of hydrogen ions in a solution. Most pH meters compensate for temperature variations. However, knowing the temperature of your sample is crucial since accurate pH values can slightly shift depending on ambient conditions.
4. Why is calibration important when using a pH meter?
Calibration ensures that your pH meter provides accurate readings by aligning its response with known standard solutions. Regular calibration improves the reliability of your results, particularly after extensive use or if the meter has been exposed to variable conditions. Aim for periodic calibration every few sessions of use.
5. Can I use different liquids to test pH using a single method?
Yes, pH measurement methods like litmus testing and pH meters can generally be applied across various liquids. However, it’s essential to clean the equipment between tests to prevent cross-contamination, which may affect the readings. Persistent residues may alter results; hence, proper technique remains vital.
6. How does pH affect chemical reactions in analytical chemistry?
In analytical chemistry, pH can determine the ionization states of compounds. This influence affects reaction rates and can dictate the outcomes of titrations and similar processes. Knowledge of pH is vital to selecting appropriate methodologies for chemical characterization and ensuring precise experimental outcomes.
7. Can I perform pH measurements in field environments effectively?
Yes, field environments can benefit from portable pH meters and colorimetric testing kits designed for outdoor use. These instruments are often built to withstand environmental variability while providing accurate readings, thereby allowing scientific safety and accuracy during field-study conditions.
Understanding how to calculate pH accurately is crucial for various scientific applications. The knowledge of pH measurement methods, alongside their significance in chemistry, biology, agriculture, and environmental science, enhances our ability to analyze and interpret the world around us. Always ensure that you’re using the best practices for measurement, maintaining accuracy for your specific needs.