Essential Guide to How to Show Hidden Files and Optimize Your Workflow in 2025
Understanding Hidden Files Across Different Operating Systems
Hidden files can often cause frustration when trying to access essential data on your computer. Whether you are a Windows, Mac, or Linux user, knowing how to show hidden files can significantly enhance your workflow and streamline file management. Hidden files typically don’t appear in regular file explorers due to certain settings that maintain system integrity. By taking the time to **uncover hidden files**, you ensure that important documents and folders are easily accessible. This guide provides step-by-step instructions for revealing hidden files on all major systems, helping you access your data whenever needed.
Showing Hidden Files in Windows
To **show hidden files** in Windows, you can utilize the built-in functionalities within File Explorer. Begin by opening File Explorer and navigating to the ‘View’ tab at the top of the window. Here, you can find options under ‘Options’ where you’ll want to select ‘Change folder and search options’. In the Folder Options dialog, switch to the ‘View’ tab, and seek out the option titled “Show hidden files, folders, and drives”. Once selected, click ‘OK’ to save your changes. This method allows you to **reveal all files** and quickly access the crucial hidden items you need.
Reveal Hidden Files Using Command Line
For those who prefer command line interfaces, you can also employ commands to **access hidden files** in Windows. Open the Command Prompt (CMD) and navigate to the directory where you suspect hidden files might be located using the cd command. Once you are in the correct folder, execute dir /a:h to show all hidden files within that directory. This command is effective for quickly discovering files that may not appear through standard navigation. Keep in mind that understanding these command line tools is an essential part of file management and optimization!
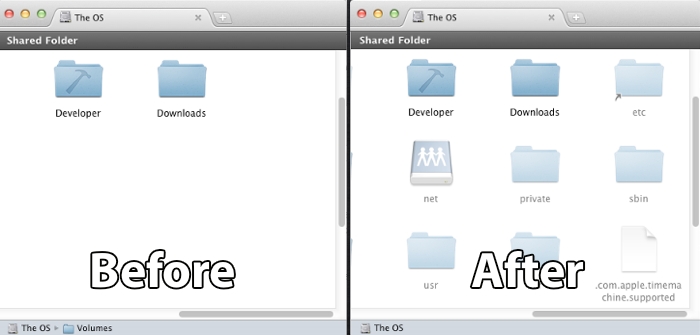
Displaying Hidden Files on Mac
Flipping to Mac systems attracts a different approach to uncover hidden files. Unlike Windows, Mac hides files for user-friendly reasons, yet there are simple ways to adjust settings. One straightforward method involves using **Finder**. Open a Finder window and press Command + Shift + Period (.). This keyboard shortcut toggles the visibility of **Finder hidden files**, making it an efficient way to quickly check for hidden folders or documents. By enabling hidden items in Finder regularly, you can maintain streamlined access to all necessary files for efficient management.
Using Terminal to View Hidden Files on Mac
If you prefer utilizing the command line, the Mac Terminal serves as a powerful tool. To reveal hidden files, launch Terminal and input defaults write com.apple.finder AppleShowAllFiles true. Follow this by executing the command killall Finder to refresh Finder and display all files. Similarly, you can use defaults write com.apple.finder AppleShowAllFiles false to revert this setting back when you’re done. Utilizing Terminal for these tasks is an effective strategy for those engaged in file management on macOS.
Accessing Hidden Files on Linux
Linux presents its own set of techniques for managing hidden files. Files and folders whose names begin with a dot (.) are typically hidden within the Linux environment. To **view hidden files** in a Linux file manager, simply open your file manager application and enable “Show Hidden Files” from the View menu. Alternatively, if you are comfortable using the terminal, you can use the command ls -a to display all files in the current directory, including those that are hidden.
Terminal Command Insights for Linux Users
Linux users can leverage robust command-line capabilities to improve file management tasks. Use the command find . -name ".*" to locate hidden files within your current folder. This command searches for any file beginning with a dot, ensuring you uncover those crucial items. Efficient command line techniques are not only time-saving, but they also promote a deeper understanding of file organization practices.
Practical Tips to Optimize Your File Management
Incorporating techniques to **show all files** and access hidden files not only aids in effective management but also enhances daily workflows. For beginners, utilizing file management software that highlights files allows for better visualization. Implement a directory structure that categorizes documents logically to avoid the common pitfall of losing files in hidden locations. You can also rely on **show file extensions** features to identify file types quickly; this prevents accidental alterations and helps maintain organization.
Organize with File Management Techniques
Practical file organization methods can significantly impact user experience. Begin by labeling your files clearly and consistently. Consider creating subfolders for project-based work to keep related documents grouped together. Utilizing cloud services to back up important files ensures that hidden files remain safely stored. Additionally, leveraging backup tools will prevent loss and provide necessary access to hidden or deleted files when needed.
Advanced Tips for Professional File Management
For advanced users, diving deeper into user interface settings allows for tailored experiences that resonate with personal workflows. Tools like scripts or automation software enable proficient handling of file visibility settings; consider services that allow you to schedule file management tasks for routine organization. Learning command line syntax can vastly improve how you control file systems and enhance your overall effectiveness in file management.
Key Takeaways
- Hidden files can be accessed readily on Windows, Mac, and Linux with appropriate settings.
- Both GUI and command line methods provide capabilities for viewing hidden files for different skill levels.
- Implementing organized file management techniques improves productivity and reduces the time spent searching for files.
FAQ
1. How do I enable hidden files on Windows?
To **enable hidden files on Windows**, open File Explorer and go to the ‘View’ tab. Click on ‘Options’, then navigate to the ‘View’ tab in the dialog box. Select “Show hidden files, folders, and drives” and confirm with ‘OK’. This process will allow you to **view hidden items** and manage them effectively.
2. Can I find hidden folders on Mac easily?
Yes, locating **hidden folders on Mac** is simple. Use the keyboard shortcut Command + Shift + Period (.) while browsing in Finder to **reveal hidden items**. This toggle feature allows for swift checking of hidden folders when necessary.
3. What command can I use to show hidden files on Linux?
To **show hidden files on Linux**, simply use the command ls -a in the terminal, which will list all files in the current directory, including those that are hidden. This is a common way to access files quickly from the command line.
4. How can I unhide files using the command line in Windows?
For Windows, you can **unhide files** via command line using the Command Prompt. The command attrib -h "filename" will remove the hidden attribute from that specific file. Replace “filename” with the actual name of your hidden file.
5. Are there risks involved in showing hidden files?
Revealing hidden files can expose sensitive operating system files or system folders. Care should be taken not to modify or delete any essential files you do not recognize, as it can lead to system instability. It’s advisable to make changes cautiously and have a backup before making adjustments.
6. How can I quickly reveal all files on a Mac?
To quickly **reveal all files** on a Mac, you can use the previously mentioned Command + Shift + Period (.) shortcut within Finder. This allows for a rapid overview of all files, helping to streamline any file searches or organization efforts.
7. What should I do if I can’t find hidden files?
If hidden files aren’t showing up after enabling visibility settings, ensure you are emptying caches or refreshing file explorers adequately. Restarting your system or utilizing command lines for specific paths can also help in locating elusive files effectively.